Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Fundoscopy Findings
Pan retinal photocoagulation is the primary treatment for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Vitreous haemorrhage may require b scan ultrasonography to determine if a tractional or rhegmatogenous retinal break or hole retinal detachment is present.
 Diabetic Retinopathy Nature Reviews Disease Primers
Diabetic Retinopathy Nature Reviews Disease Primers
Fundoscopy allows the ophthalmologist to detect retinal degeneration detachment and other abnormalities of the blood vessels and the optic nerve.

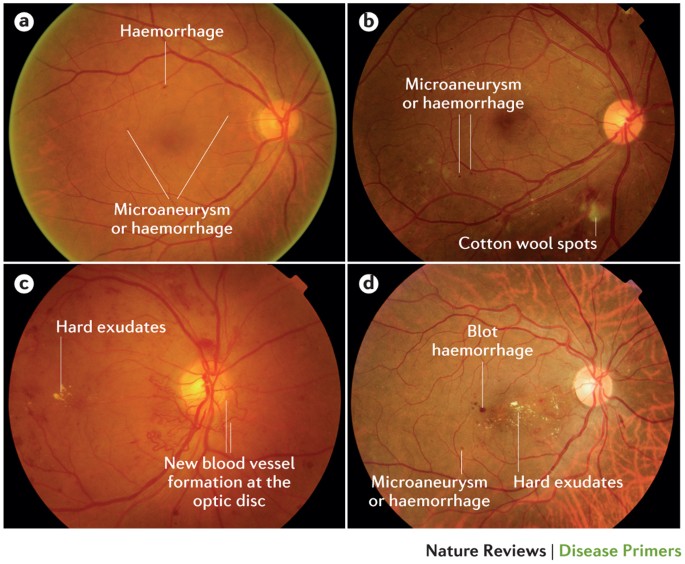
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy fundoscopy findings. Diabetic maculopathy diabetic retinopathy situated in and around the macula is described as diabetic maculopathy which can result in significant visual impairment. The unchecked progression of proliferative diabetic retinopathy can lead ultimately to tractional retinal detachment which may or may not involve the macula. The central retinal area can develop abnormal findings in diabetic retinopathy.
It may lead to vitreous hemorrhage and traction retinal detachment. Proliferative retinopathy is characterized by abnormal new vessel formation neovascularization which occurs on the inner vitreous surface of the retina and may extend into the vitreous cavity and cause vitreous hemorrhage. Two or more of the criteria for severe non proliferative diabetic retinopathy but without any proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
These changes in the macula include the presence of abnormally dilated small vessel outpouchings called microaneurysms retinal bleeding retinal hemorrhages and yellow lipid and protein deposits hard exudates. The fundus consists of the retina the macula the optic nerve and blood vessels. Fundoscopy or ophthalmoscopy is a test done to examine the back of the eye and the inner lining.
Proliferative retinopathy develops after nonproliferative retinopathy and is more severe. As part of screening tests a fundoscopy is performed to look for the presence of diabetic retinopathy. These findings can be present in the non proliferative or the proliferative forms of the disease.
Clinically it is seen as clusters of burn marks on the retina which have been created by the laser used in the treatment process. The rationale behind the treatment is to reduce the production of vegf by reducing the oxygen demand from the peripheral retina.
 Diabetic Retinopathy Eye Disorders Merck Manuals Professional
Diabetic Retinopathy Eye Disorders Merck Manuals Professional
 Emergency Atlas Of Diabetic Retinopathy Free Medical Atlas
Emergency Atlas Of Diabetic Retinopathy Free Medical Atlas
 Diabetic Retinopathy Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
Diabetic Retinopathy Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
 Diabetic Retinopathy Features Of Diabetes Hard Exudates
Diabetic Retinopathy Features Of Diabetes Hard Exudates
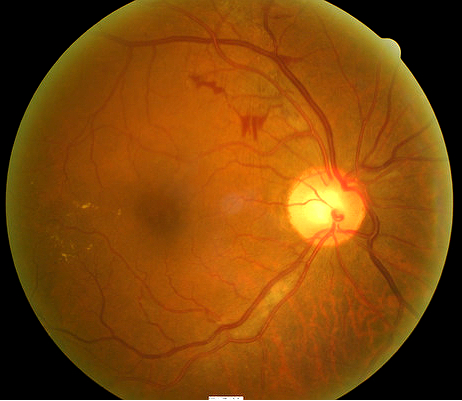 Diabetic Retinopathy Without Macular Edema Decision Maker Plus
Diabetic Retinopathy Without Macular Edema Decision Maker Plus
Comments
Post a Comment